Unlocking the Power of Data Visualisation in Business Intelligence


Data visualisation is essential to business intelligence (BI), enabling businesses to transform complex data into actionable insights. In today's data-driven world, organisations must be able to quickly and effectively analyse data to make informed decisions that drive growth and success.
However, analysing large volumes of data can be challenging, especially if the data is presented in a raw, unstructured format.
This is where data visualisation comes in – by submitting data in a visual form, users can quickly and easily identify trends, patterns, and outliers and then make informed decisions based on the insights generated.
In this article, we will explore the importance of data visualisation in BI and look at some of the critical benefits and tools businesses can use to leverage the power of data visualisation. We’ll also discuss best practices for creating compelling data visualisations and offer strategies for optimising your BI initiatives with visualised data.
The basics of BI
Business intelligence refers to the processes, methods, and technologies used to collect, integrate, analyse, and present business information. BI aims to help organisations make better business decisions by providing insights into their operations' past, present, and future performance.
BI solutions enable businesses to collect and analyse large amounts of data from various sources, including internal systems, external databases, and social media platforms, in order to identify patterns and trends and to gain insights into customer behaviour, market trends, and industry best practices.
There are several key components to a successful BI strategy, including data integration, data warehousing, data mining, data visualisation, and reporting.
Data integration
Data integration involves collecting and consolidating data from multiple sources into a single database or data warehouse. It allows businesses to comprehensively view their operations and analyse data across different departments and functions.
Data warehousing
Data warehousing involves storing and organising data in a central repository, which BI tools and applications can access.
Data mining
Data mining is the process of analysing data to identify patterns and trends, extracting valuable insights that can be used to drive business decisions. It involves using statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to uncover hidden relationships and correlations between different data points.
Data visualisation
Data visualisation refers to using data visualisation charts, graphs, and other visual aids to represent complex data in a way that is easy to understand and interpret. This allows users to quickly identify trends and patterns and make data-driven decisions for their business based on the insights generated by BI tools.
Reporting
Reporting is an essential component of any BI solution, as it allows businesses to communicate the insights generated by BI tools to decision-makers across the organisation. Reports can be generated in various formats, including dashboards, scorecards, and ad-hoc reports, and can be customised to meet the specific needs of different stakeholders.
Why BI is vital
In summary, business intelligence is critical to modern business operations. It gives organisations the insights and tools they need to make data-driven decisions and stay competitive in today's fast-paced business environment. By leveraging BI technologies and processes, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their operations, identify areas for improvement, and make strategic decisions that drive growth and success.
We will focus on the data visualisation component in this article as it is especially important for successful BI implementation.
Advantages of data visualisation
Simply put, data visualisation aims to give business users a visual representation of their data. They can then make informed decisions based on the insights generated.
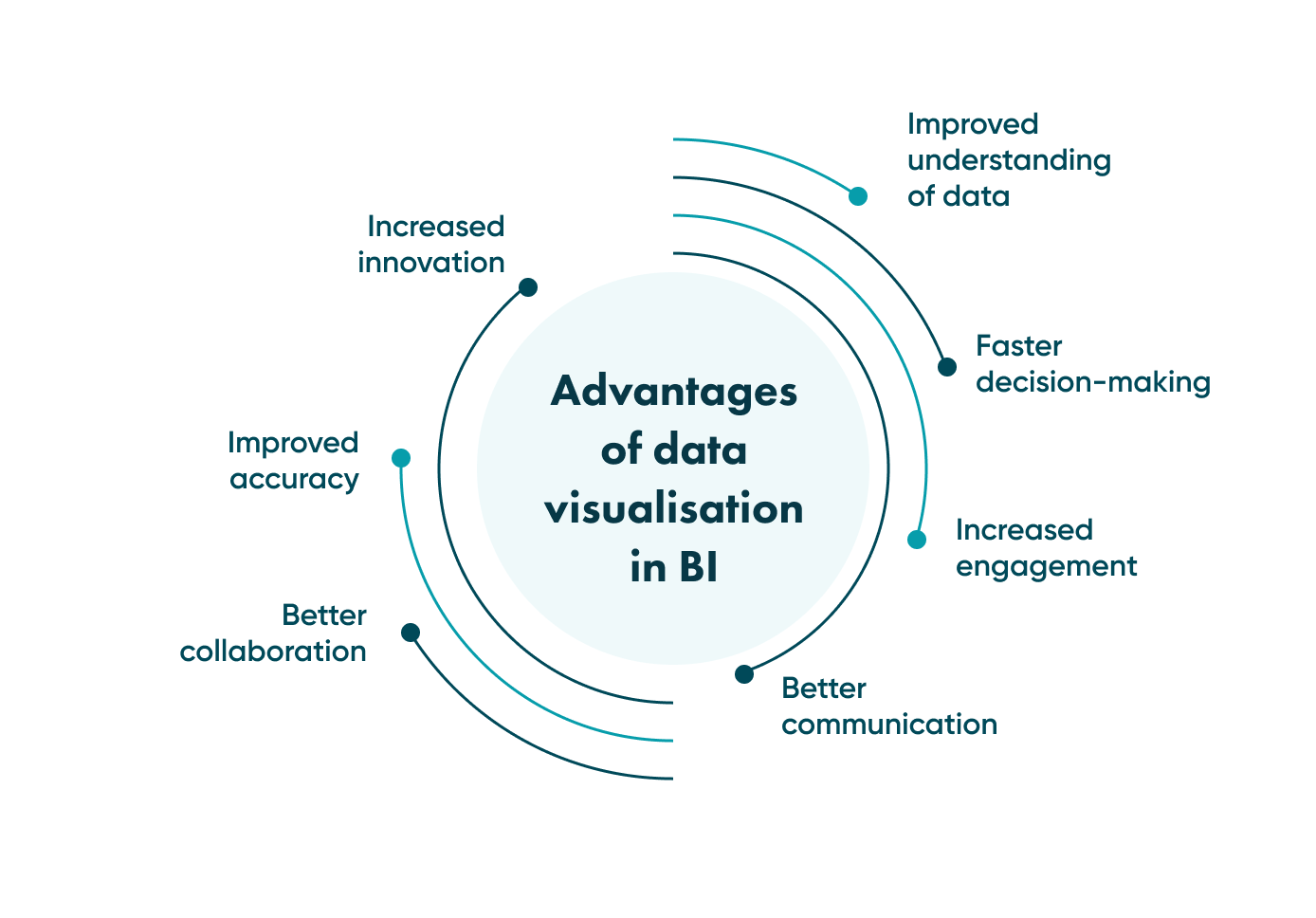
Improved understanding of data
Data visualisation tools make it easy for users to see and understand their data, even if they are not experts in data analysis. By presenting data in a visual format, users can identify trends, patterns, and outliers that may be difficult to spot in a spreadsheet or database.
Faster decision-making
Data visualisation allows business users to quickly identify significant trends and patterns in their data, which can help them make informed decisions more quickly. It can be imperative in fast-paced industries where decisions must be made promptly to stay ahead of competitors.
Increased engagement
In addition, visualised data can make data more engaging and exciting, which can help increase user engagement and adoption of BI tools and applications. This can heighten user satisfaction and lead to more effective BI tools and data use.
Better communication
Data visualisation can be an effective tool for communicating complex data to stakeholders and decision-makers. By presenting data in a visual format, users can quickly understand the key insights and implications of the data, leading to better decision-making and more effective communication.
Better collaboration
Data visualisation techniques facilitate cooperation among team members, allowing them to work together to analyse and interpret data. This can result in better teamwork, improved problem-solving, and more effective use of data across the organisation.
Improved accuracy
Another advantage lies in improving the accuracy of data analysis by making it easier to identify errors and outliers in the data. With visualised charts and graphs, users can quickly zero in on discrepancies and outliers that may have been missed in a spreadsheet or database.
Increased innovation
Visual analytics tools can spur innovation by giving business users new insights and perspectives on their data. By visually presenting data, users can identify recent trends and patterns that were not previously apparent, leading to new ideas and innovations.
How data visualisation plays into software development
How can data visualisation help us when we create your software? There are three main advantages of BI visualisation tools during web or mobile app development.
Testing and optimisation
Apart from the advantages mentioned above, data visualisation can be a powerful tool for testing and optimising software. Software developers can quickly identify issues or opportunities for improvement and make changes to their software accordingly.
Monitoring and troubleshooting
Visualisation tools also help monitor software performance and troubleshoot issues. As a result, developers can quickly identify problems or anomalies and take action to resolve them.
Enhancing user experience
By analysing data on user behaviour, developers can gain insights into how users interact with their software and make changes to improve the user experience. Data visualisation can help developers quickly determine patterns in user behaviour, and make informed decisions about optimising their software for maximum usability.
What else do you need to know about software development? We will provide a detailed consultation — contact Go Wombat.
Data visualisation types
There are a variety of data visualisation types, but we will focus on the most frequently used ones here.
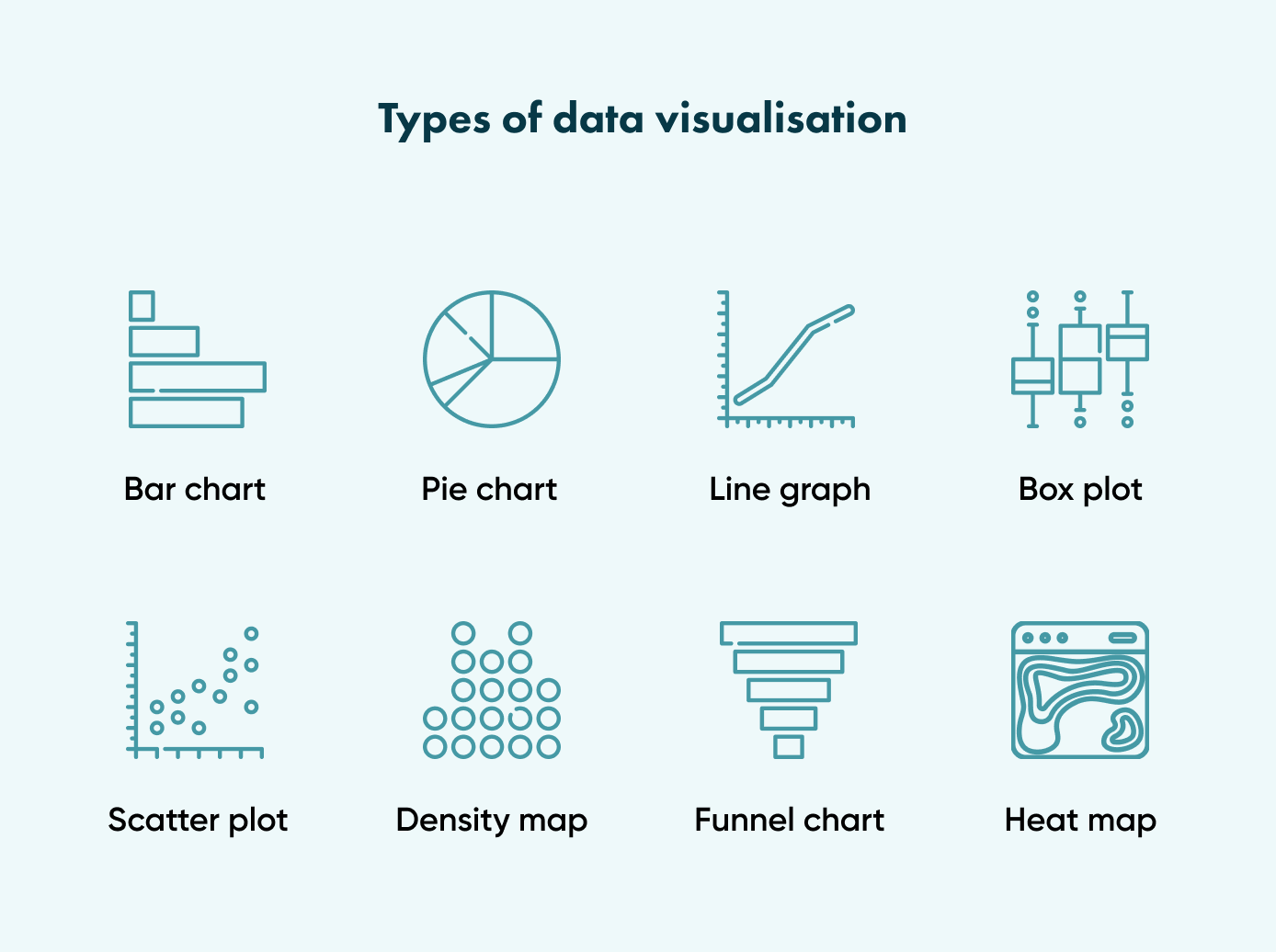
Bar chart
A bar chart is a fundamental method for comparing data units. Due to its straightforward graphic format, it is commonly used in BI as an interactive page component. This data visualisation chart can be adapted to display more intricate data models, with bars organised into clusters or stacks to demonstrate the distribution across market segments or subcategories. This same flexibility applies to horizontal bar charts, better suited for displaying long data labels on the bars.
Pie chart
Another widely used chart is the pie chart, which is often used in marketing or sales departments to illustrate the composition of objects or for unit-to-unit comparisons.
A pie chart is a circular graph divided into sectors, each representing a proportion of a whole. The size of each sector is proportional to the value it represents, and the sum of all sectors adds up to 100%.
Pie charts are commonly used to display the composition of a single data set, where each sector represents a category or subcategory of the whole. They can help highlight each category's relative sizes and show how they contribute to the full scope.
While pie charts are popular because of their simplicity and visual appeal, there may be better types of data visualisation for displaying large data sets or comparing data across multiple variables.
Line graph
A line graph uses a horizontal and a vertical axis to show the variation of a unit over time. Line data visualisation graphs can be combined with bar charts to represent data with more dimensions.
Box plot
Although a box plot may seem complicated at first glance, upon closer inspection, it becomes clear that it represents quarters in a horizontal format. The main elements of a box plot are the minimum and maximum values, with the median placed between the first and third quartiles.
The purpose of a box plot is to display the distribution of objects and their deviation from the median.
Scatter plot
This type of visualisation is created using X and Y axes, with dots representing objects placed in between them. The position of a dot on the graph indicates its specific qualities. Like line graphs, dots placed between the axes are easily recognisable. The main limitation of this visualisation is the number of axes that can be used.
Dot map/density map
Overlaying a visualisation onto a map effectively displays data in its geographical context. Density maps are created by placing dots on the map to indicate the location of each unit. A single dot can represent an individual unit, such as a marketplace, or a cluster of objects in a particular area.
While this format makes density easy to perceive, it may not provide precise numerical values.
Funnel charts
Funnels are ideal for illustrating decreasing correlations among various groups of items. Typically, funnels employ both geometric shapes and colour coding to distinguish objects. This chart type is beneficial when there are multiple stages in a process.
Heat maps
A heat map is one of the widespread data visualisation examples, representing the magnitude of a phenomenon in 2 dimensions using colour. The colour variation, which can be in hue or intensity, provides clear visual cues to the reader about how the phenomenon is clustered or fluctuates over space.
There are 2 main types of heat maps: cluster heat maps and spatial heat maps.
In a cluster heat map, magnitudes are arranged into a matrix with fixed-cell size, where the rows and columns represent discrete phenomena and categories.
A spatial heat map uses colour to represent the density or distribution of a phenomenon across a geographical area. It displays data in a map format, where the intensity of the colour is proportional to the frequency or magnitude of the occurrence in that particular region.
Data visualisation tools
There are many data visualisation tools available in the market today. Let’s look at the tools our own business analysts use the most during the discovery phase.
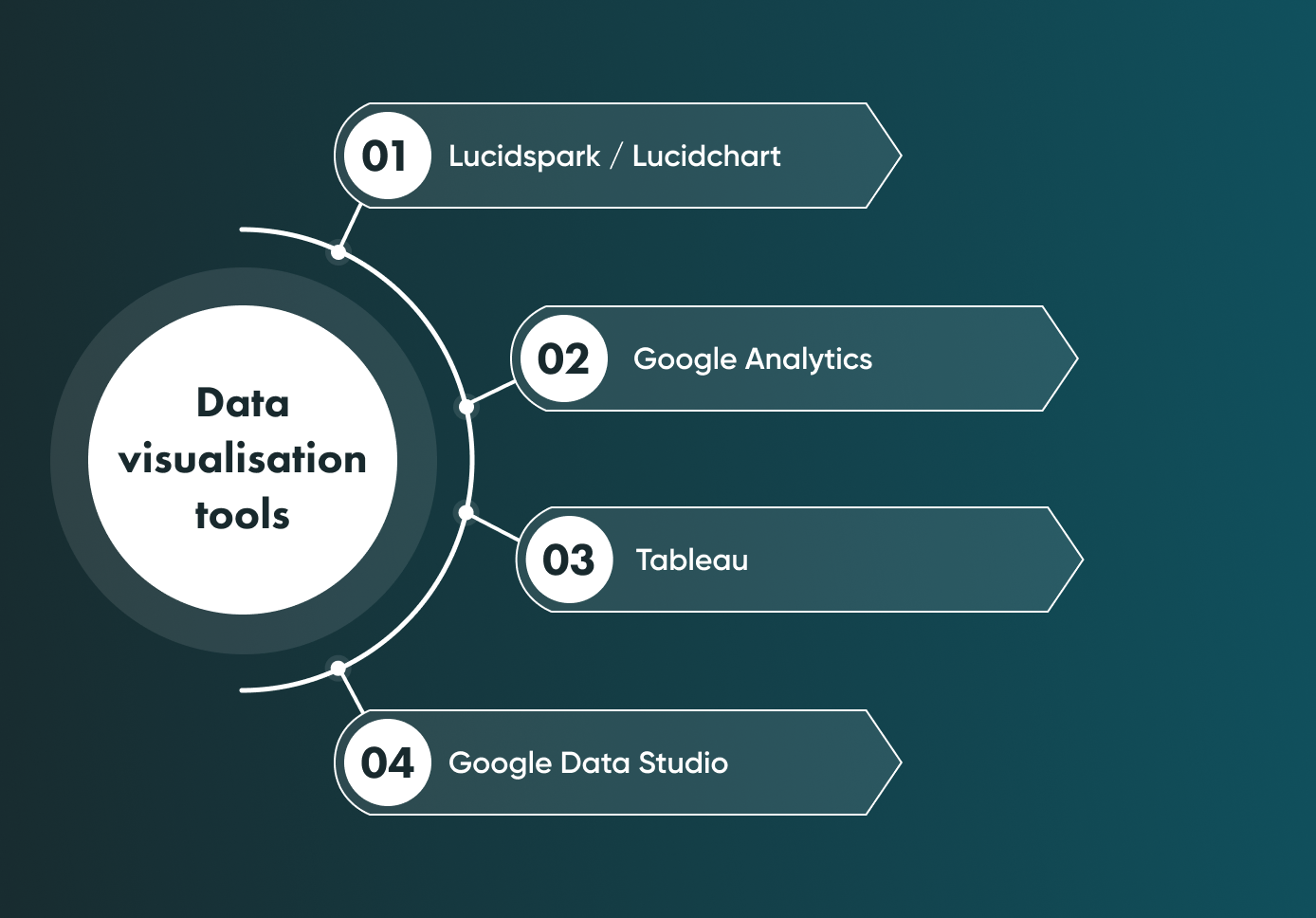
Lucidspark/Lucidchart
Lucidspark and Lucidchart are 2 cloud-based software tools developed by Lucid, a company specialising in visual collaboration software. Lucidspark and Lucidchart offer similar collaboration features, including real-time editing and commenting as well as access control.
Lucidspark
Lucidspark is a virtual whiteboard platform that allows teams to collaborate in real-time and brainstorm ideas using various multimedia tools such as sticky notes, freehand drawings, and pre-built templates. In addition, it offers features like integration with other collaboration tools, voting on ideas, and real-time collaboration.
Lucidchart
Lucidchart is a web-based diagramming application that allows users to create professional-looking diagrams and flowcharts. It provides many templates and shapes for business, engineering, and education. It is integrated with other tools such as Google Drive, Dropbox, and Slack and offers real-time collaboration, data linking, and publishing options.
Google Analytics
At Go Wombat, we also use Google Analytics when working on your project. It is a powerful tool for tracking website traffic and user behaviour. While it provides various data visualisations within the platform such as line graphs, pie charts, and tables, it does not specialise in creating charts and graphs for data analysis purposes.
However, Google Analytics provides the necessary data for users to export and analyse using other visualisation tools, such as Google Data Studio or Tableau. These tools can connect to Google Analytics, allowing users to create more advanced, interactive charts and graphs to gain insight into their website's performance.
Tableau
Tableau is one of the most popular data visualisation tools examples available today. It provides multiple features and capabilities, including drag-and-drop functionality, interactive dashboards, and real-time analytics.
Google Data Studio
Google Data Studio is a free tool offered by Google. It allows users to create customisable and interactive reports and dashboards using data from various sources, including Google Analytics, Google Sheets, and many other data connectors. Data Studio allows users to create different types of data visualisation charts, graphs, tables, and other visualisations in order to analyse and share data with stakeholders.
Primary data visualisation techniques and practices
Finally, let’s discuss the leading data visualisation practices in business intelligence.
#1. Define your goals
Before creating a visualisation, define your goals and objectives. It will help you identify the key insights you want to convey and ensure your data visualisation is focused and effective.
#2. Keep it simple
Straightforward data visualisations are often the most effective. Avoid cluttering your visualisation with unnecessary information or decorative elements that can distract from the key insights.
#3. Choose the correct type of visualisation
Different data analytics and visualisation are better suited to varying types of data and insights. Ensure you choose the right visualisation type for your data to connect your insights effectively.
#4. Use colour and contrast wisely
Colour and contrast can be powerful tools for highlighting key insights and patterns in your data. Use colour and contrast strategically to draw attention to the most critical information.
#5. Provide context
Providing context is essential to help users understand the meaning and significance of the visual data analysis presented. Include appropriate labels, titles, and annotations to provide context and help users interpret the data correctly.
#6. Make it interactive
Interactive data visualisations can be a great way to engage users and enable them to explore data more deeply. Consider using interactive elements such as filters, hover-over text, and drill-down capabilities to allow users to analyse data in more detail.
#7. Test and refine
Like any aspect of BI, data visualisations should be tested and refined over time to ensure that they are effective and provide value to users. Regularly review your data visualisations and make necessary changes to ensure they meet your goals and objectives.
#8. Ensure accessibility
Finally, it is crucial to consider accessibility when creating data visualisations. Ensure your visualisations are easy to read and understand, and consider providing alternative formats for users with visual impairments or other accessibility needs.
Summing up
Clearly, data visualisation is a powerful method for businesses to make informed decisions and gain valuable insights from their data. Companies can quickly and easily analyse complex data sets, identify patterns and trends, and communicate their findings with stakeholders through interactive charts, graphs, and dashboards.
That said, you should keep in mind that effective data visualisation requires both technical skills and an understanding of data analysis and interpretation. It is also crucial to ensure data is accurate and reliable before presenting it through visualisations.
This is where Go Wombat can help you. We can build the right tools to simplify the visualisation process or integrate other BI solutions into your software. Data visualisation is only one solution among many others.
Ready to take your business to the next level? Let us help you develop high-quality software solutions tailored to your specific needs. Contact Go Wombat!
Unlock Success with Premium Software Development
Contact us


FAQ
Why is data visualisation important in business intelligence?
When you visualise data in business intelligence, you provide an improved understanding of data, which contributes to a faster decision-making process, enhanced engagement, better communication and collaboration. Moreover, it enables improved accuracy and increased innovation.
What are the main goals of data visualisation?
The main goals of data visualisation are:
- To help people understand and interpret complex data easily and quickly.
- To facilitate effective decision-making based on insights derived from data analysis.
- To provide data-driven insights and trends clearly to stakeholders and audiences.
- To identify patterns, relationships, and outliers in data that may not be visible through other means.
- To support identifying opportunities and areas for improvement in businesses, organisations, and processes.
- To enhance data storytelling and make data more engaging and impactful for audiences.
What are data visualisation examples for business?
You can find multiple examples of data visualisation. However, the primary and most frequently used visualisation types are bar charts, pie charts, line graphs, box plots, scatter plots, dot maps, funner charts, and heat maps.
How can we help you ?



