6 GDPR Compliance Principles You Need to Master


The cost of not understanding or following the GDPR principles is too high to ignore.
According to GDPR.EU, noncompliance with GDPR principles can lead to fines of up to 4% of a company’s global turnover.
Even so, deciding how or where to start the implementation of GDPR best practices is difficult.
This article is a follow-up to our previous piece on GDPR regulations, and its purpose is to provide additional information about the principles of these laws and what they mean for your business.
We’ll also tell you how the GoWombat team can help you evaluate all relevant variables before you start implementing GDPR best practices.
How to prove compliance and protect personal data
Regardless of their industry, most companies collect users' online information in various ways.
Whether it’s a hospital, a bank, or a school, all these organizations collect and process vast amounts of data.
This data is used for companies' benefits and for running routine work processes. But, now these organizations also have to prove that they are following safety best practices when collecting this information.
The best way to prove compliance is to follow the steps outlined in the Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) on the GDPR site.
What is GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a part of EU law on data privacy protection. The GDPR is essential for companies with EU licenses and business and non-profit organizations that collect and store users' personal data.
It's important to clarify that GDPR protects the rights of all EU and UK citizens. The GDPR is widely used in the European Economic Area.
The GDPR requires a long process, not to mention the fact that its details and specifics depend on the country where the business is registered and that nation’s legislation.
What is the purpose of GDPR?
In short, it is the protection of information that can be used to identify individuals on a personal level.
GDPR controls the organizations that collect this kind of information and use it for their own purposes.
It’s important to note that the GDPR protects personal data mainly. Personal data means everything that could help identify an individual person.
Meanwhile, anonymous or non-personal data are out of the GDPR jurisdiction. The reason behind this is an inability to identify any person with this type of information.
This means that any collection method or tool that collects personal information in the European region has to follow GDPR compliance.
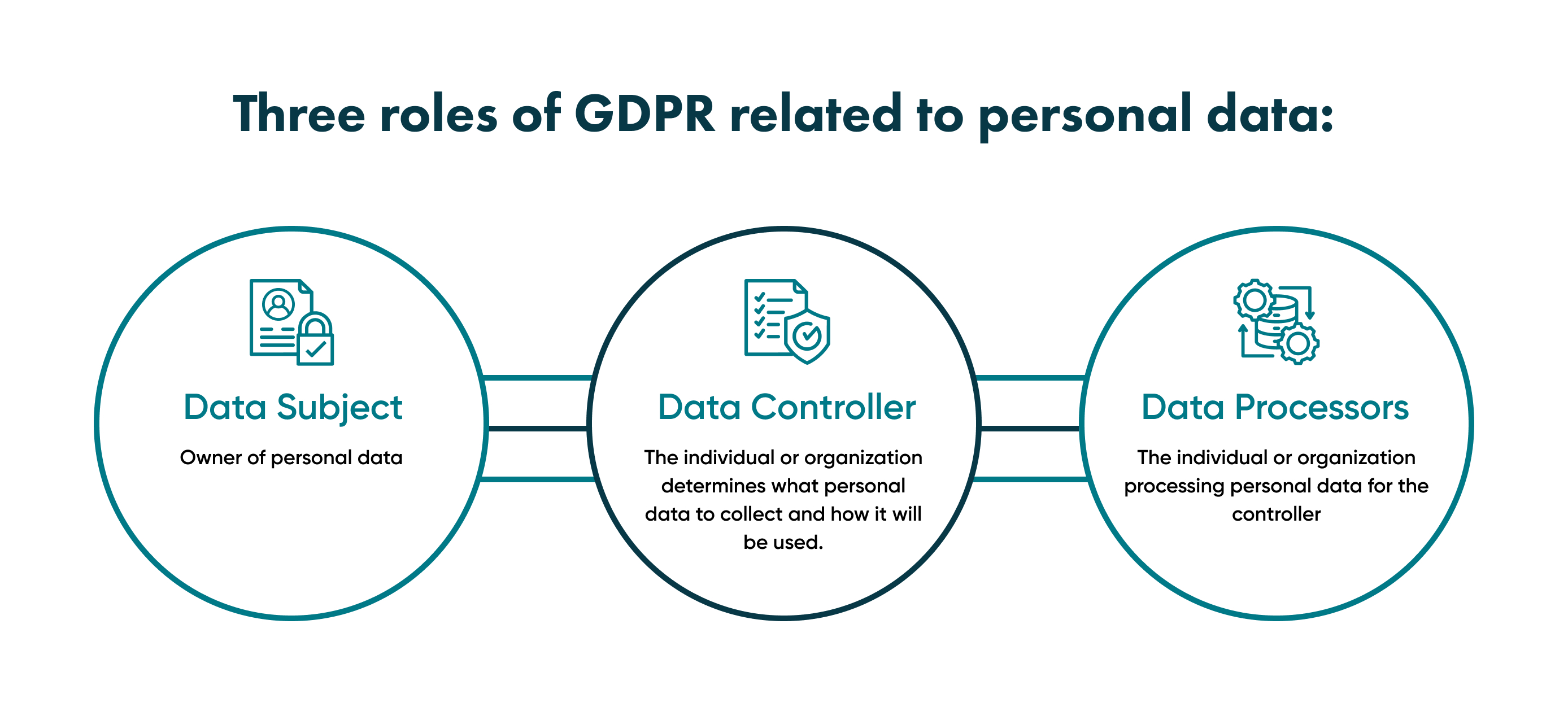
Here are three key concepts you need to know in order to understand GDPR laws.
Data subjects
These are the owners of personal data, the individual that you are collecting information about.
In practice, it's the person or organization whose privacy and data safety rights should be protected by the GDPR.
Data processor
It's an organization or individual responsible for processing personal data for the data controller. In essence, it’s the tool or organization that collects the data.
Data controller
It's the party that collects personal data and uses it for its purposes. If you are a business owner with a website that collects information, you are a data controller.
What are the six principles of the GDPR?
There are 6 key principles that will help you understand the GDPR and what it’s designed to achieve.
These are:
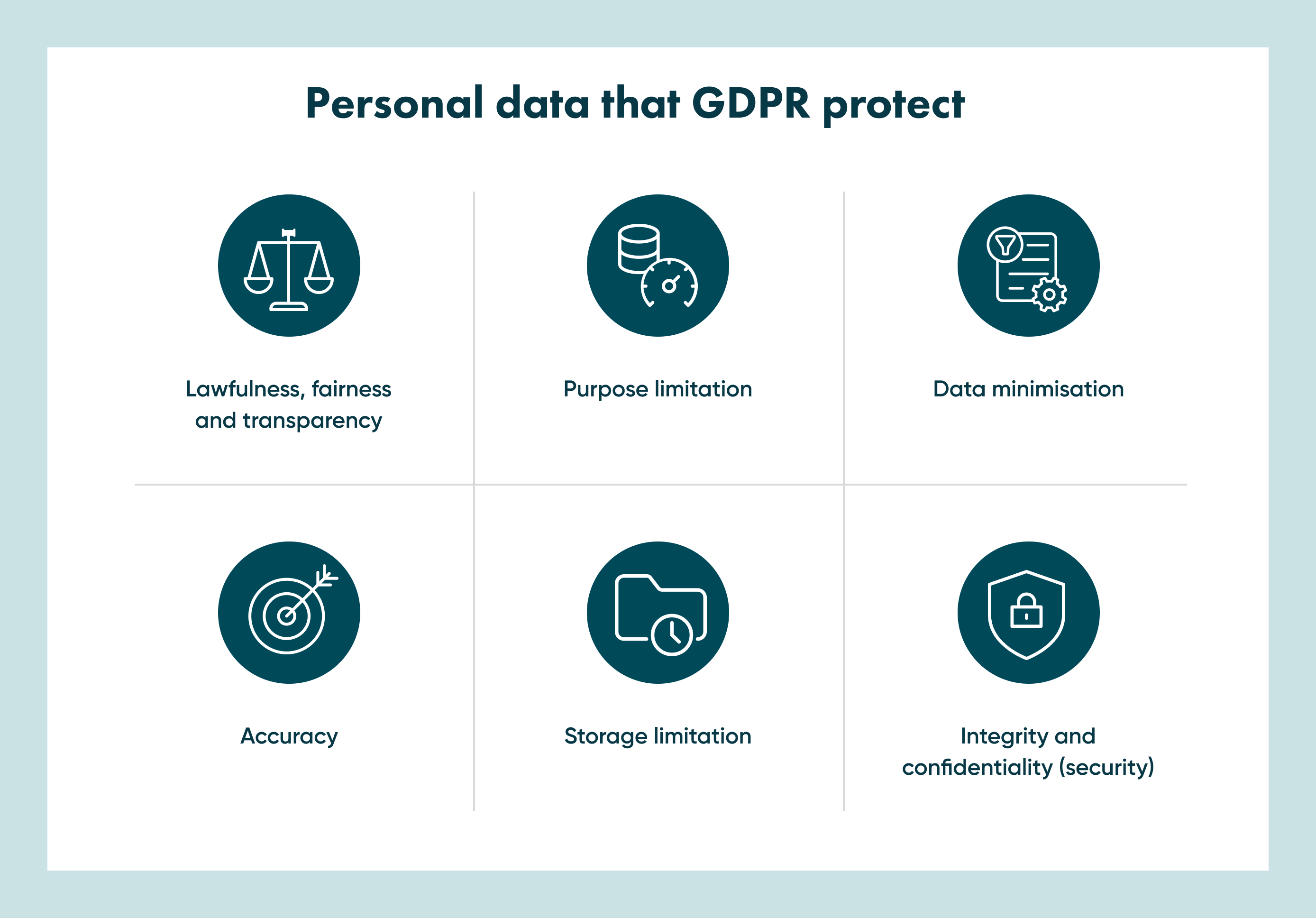
1. Lawfulness, fairness and transparency
According to the first GDPR principle, your company must treat users' data in compliance with the law.
An important detail of this principle is fairness. It's not enough to collect the data subject's information in good faith. Rules and rights have to be clearly explained to data subjects.
So, companies' privacy policies should transparently explain what kind of data they collect and why.
The privacy policy, which is a part of the first rule of compliance, must give complete information about what types of data you collect, why you need the data, how you process the data, and whether you intend to share the data with a third party.
Remember, the country where the organization is registered may have unique laws on collecting and using personal data.
2. Purpose limitation
The GDPR principles protect the subject's data from overuse. Therefore, you can only collect data related to the purpose you’re using as a justification.
Moreover, storing this data is limited. Data should only be stored for the purpose of learning from the information, rather than monetizing it directly.
3. Data minimisation
Organizations have the right to collect and process personal data, but only if it’s relevant and absolutely required. In other words, companies need a legitimate purpose, written consent, or a system to anonymize the data before its analyzed.
The advantage of this rule is limited access to sensitive data within the company and easy storing and updating processes.
4. Storage limitation
Once collected, users' personal data must be stored only for a certain amount of time. This is usually the most minimal term that a company needs to use for stored data, although the standard varies from industry to industry.
Afterward, personal data has to be properly deleted. To follow this rule, data collectors can't sell emails or phone numbers to third parties or use them to automatically create accounts without the data subject's permission.
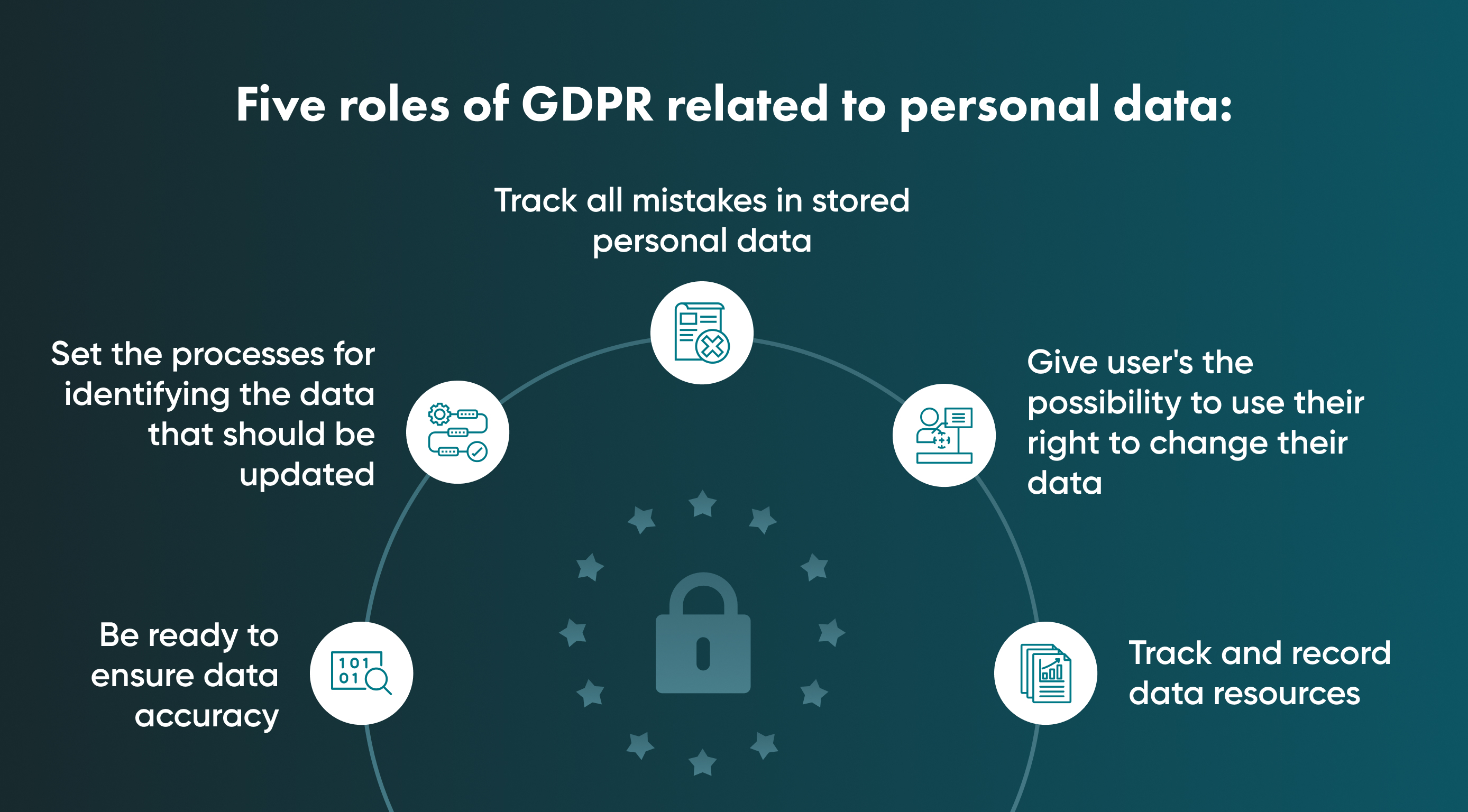
5. Accuracy
The party that collects and stores people's personal data is responsible for accuracy guarantees. This also means that the company should take reasonable and lawful steps to achieve data accuracy if needed.
Data must be accurate enough to not lead to any misunderstandings.
Follow the next rules to stay compliant with the data accuracy principle:
-
Create a plan to ensure data accuracy.
-
Set the processes for identifying the data that should be updated.
-
Track all mistakes in stored personal data.
-
Give user's possibility to use their right to change their data.
-
Track and record data resources.
6. Integrity and confidentiality
The data holder should ensure data subjects that their personal information is stored securely and provide evidence of safety levels. Moreover, the company can't collect data that couldn't be stored according to cybersecurity and information safety standards.
Bonus principle: Accountability
To prove accountability, the company or individual should show they have data safety documentation.
Accountability might be checked by a DPO (data protection officer). Also, there are a bunch of documents and standards on GDPR compliance.
This list includes, ISO 27001, ISO 27701, and PCI DSS.
Why are GDPR principles important?
The GDPR laws were created to ensure that the internet is a safe space for everyone and that no malicious party can benefit from unethical practices, like the collection and illegal sale of user data.
Not only this, but it also helps humanize digital users and ensure that their rights are being guaranteed, even while surfing the web.
Data subject rights compliance
The graphic below helps us illustrate the right that data subjects have.
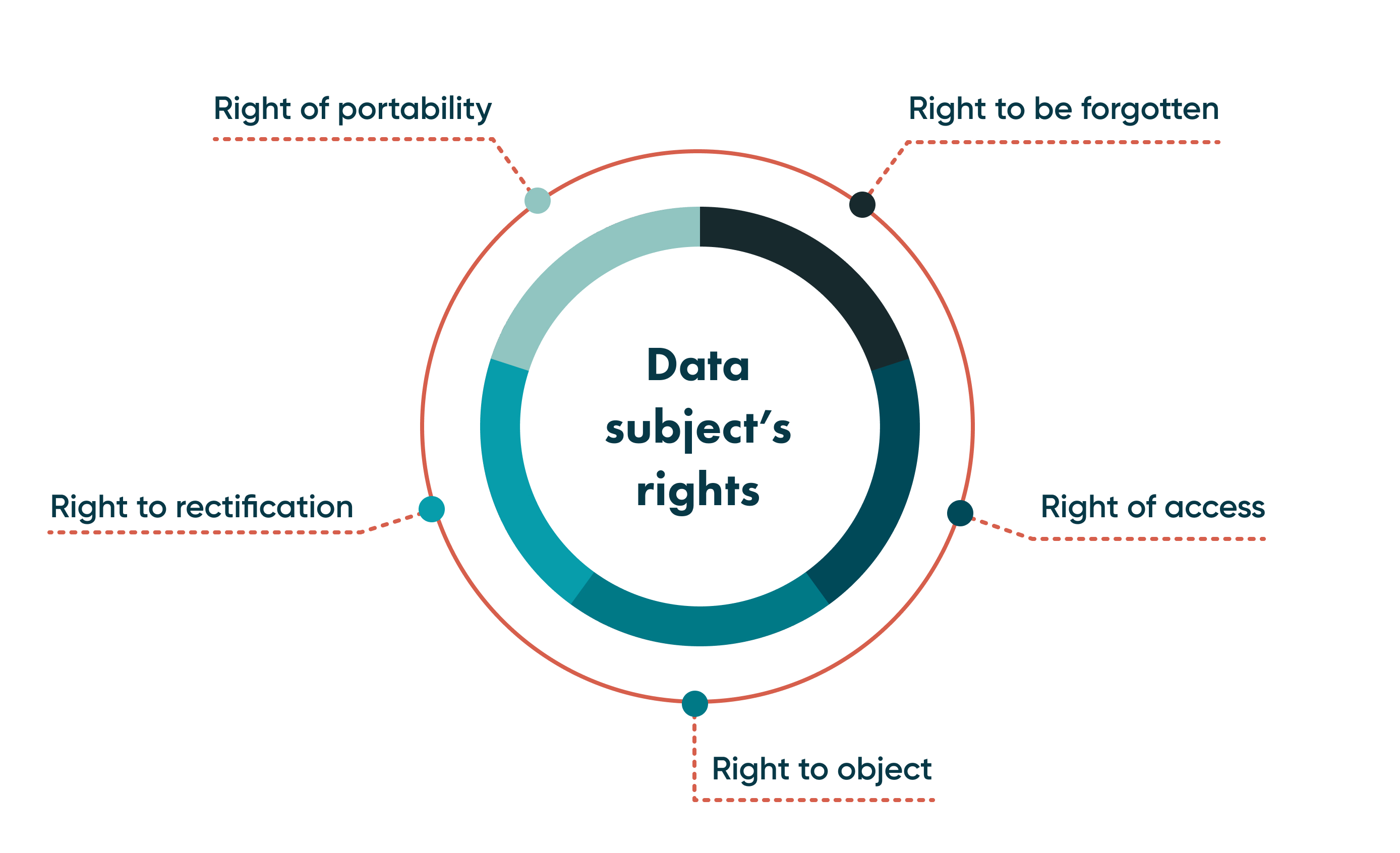
In other words, what the people that you collect information from are entitled to under GDPR rules.
These protocols are: right to portability, right to be forgotten, right to rectification, right of access, and right to object.
Right to be forgotten
All data subjects have a right to have their personal data erased from the storage they can’t lawfully access.
The right to access
Law protects users' will to access their sensitive personal data on request. Also, access to stored data might be asked for during trials by lawyers.
However, this right can be denied by data collectors if national security or law enforcement gives reasons to break it.
The right to object
All data subjects have a right to refuse to give their personal information. However, companies can decline those objections if the organization can satisfy the legal conditions of GDPR.
In this case, the party who collects the data should notify the subject and explain the reasons behind declining.
The right to rectify
Human error leads to mistakes in personal data.
Therefore, as a responsible party, the website owner needs to give the possibility to rectify mentioned mistakes in the subjects' data.
The right of portability
All personal data the company collects and stores can be asked to be removed or transferred to third parties upon the data subject's request.
Who is the subject of GDPR compliance?
According to the general definition, the subject of GDPR compliance is the person or company whose data was collected and processed by a second or third party.
Meanwhile, the data subject is a person who has personal information that organizations could use.
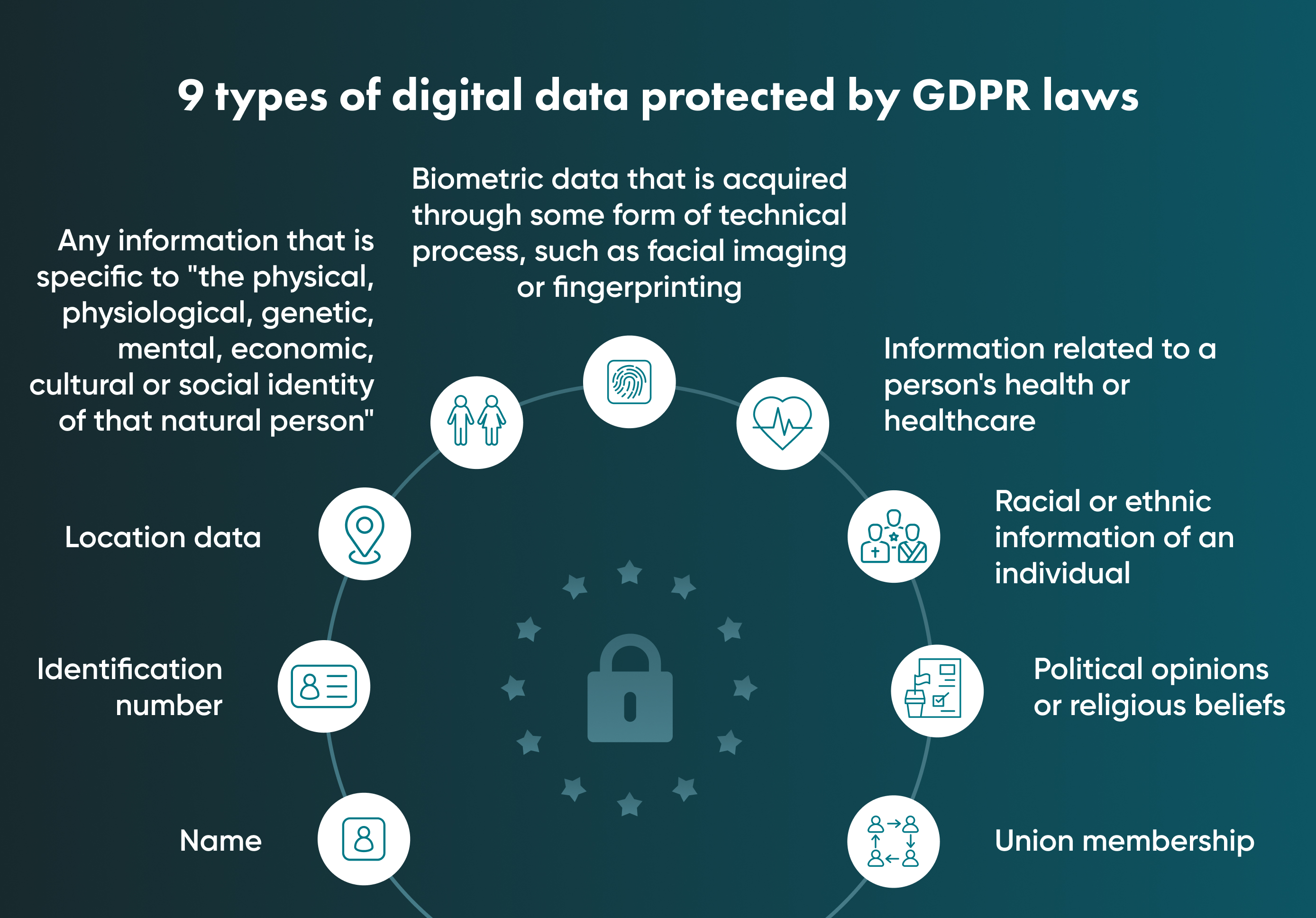
How do small and medium businesses benefit from the GDPR?
GDPR regulations have a positive impact for SMBs, which is seen on two fronts: a growth in client trust and the minimization of legal issues.
Gaining clients' trust
Users need to be sure they control their data.
The need to manage and protect personal data became a consumer priority when cloud data thefts and blackmailing became a part of a new reality.
The GDPR rules and businesses that follow them empower users to feel in control.
Avoiding damages and lawsuits
Whatever the company's final goal is, the data collector is always responsible for not disseminating the information obtained.
Noncompliance with the GDPR leads to fines from governments and compensations for customers. It’s a losing battle for companies.
GoWombat can help you to evaluate your company’s needs and make sure that you comply with the GDPR successfully.
Go Wombat's experience
The steps we take to implement GDPR compliance follow a similar logic, but the details are specific and customized to each client.
Consultation first
Before setting any strategy, we have to understand your business needs. We gather information on your business industry and niche, what budget you can create for GDPR compliance, and all other relevant variables.
Next, we check how much work we have on our way to fulfilling your needs. Sometimes, it might be website development according to GDPR or work on the application. Something our clients only need is the creation of a privacy policy.
Whatever you need, we'll make sure you have it and that it complies with all GDPR mandates.
Risk assessment and gap analysis
The risk assessment and gap analysis process makes up a crucial stage in the implementation process.
Our specialists calculate individual risks and develop ways to overcome them.
The last stage of work is the implementation of GDPR compliance with the optimal methods for the customer.
What can you get for data protection within your company?
When partnering with Go Wombat, you can get:
- Privacy policy creation. This document is a customized inner security "law" that covers your business needs.
- Internal GDPR compliance management.
However, our team doesn’t manage the physical level of data security.
Unlock Success with Premium Software Development
Contact us


Conclusion
In a nutshell, GDPR is a collection of regulations whose end purpose is the protection of people's personal data.
GDPR became the new important rule of the game and every player should be aware of it. Moreover, strong GDPR principles of compliance will benefit you with a well-composed Privacy Policy.
Changes in law require quick business response and adaptation. Also, users' awareness and knowledge about their rights naturally increase.
It will encourage companies to adhere more strictly to principles of GDPR compliance.
Contact Go Wombat if you need help understanding what level of compliance and protection of sensitive data is necessary in your particular case.
Then, our team of professionals will provide you with GDPR compliance and data protection you need.
*Note: we do not provide data security on a physical level.
How can we help you ?




