What Sustainable Manufacturing Looks Like with AI and Data Automation


The shift to a greater demand in sustainable manufacturing is largely powered by AI and data automation. Businesses, in their droves, are implementing green manufacturing processes as a response to eco and operational challenges. The dire need to avert climate change serves as a major factor in the industry's decision to accept new technologies like AI, smart automation, and renewable energy as the most effective means to achieve modern sustainable manufacturing.
These are the tools that enable manufacturers to consume energy optimally, lessen waste, and increase operational efficiency without causing more harm to the environment. Through the use of AI-powered solutions and manufacturing analytics, traditional methods can be overhauled into viable production systems that are both eco-friendly and economically sustainable.
Why Sustainable Manufacturing Matters Today
Sustainable manufacturing includes the production of goods in such a way that the processes used are efficient and do not harm the environment. Such sustainability efforts aim to reduce waste, emissions, and energy consumption. Industry is the main culprit for nearly 20% of the global CO2 emissions. Hence, manufacturing companies must rapidly change their operations to reduce their impact on the environment if they are to stay in business, or else they will be exposed to regulatory, reputational, and financial risks.
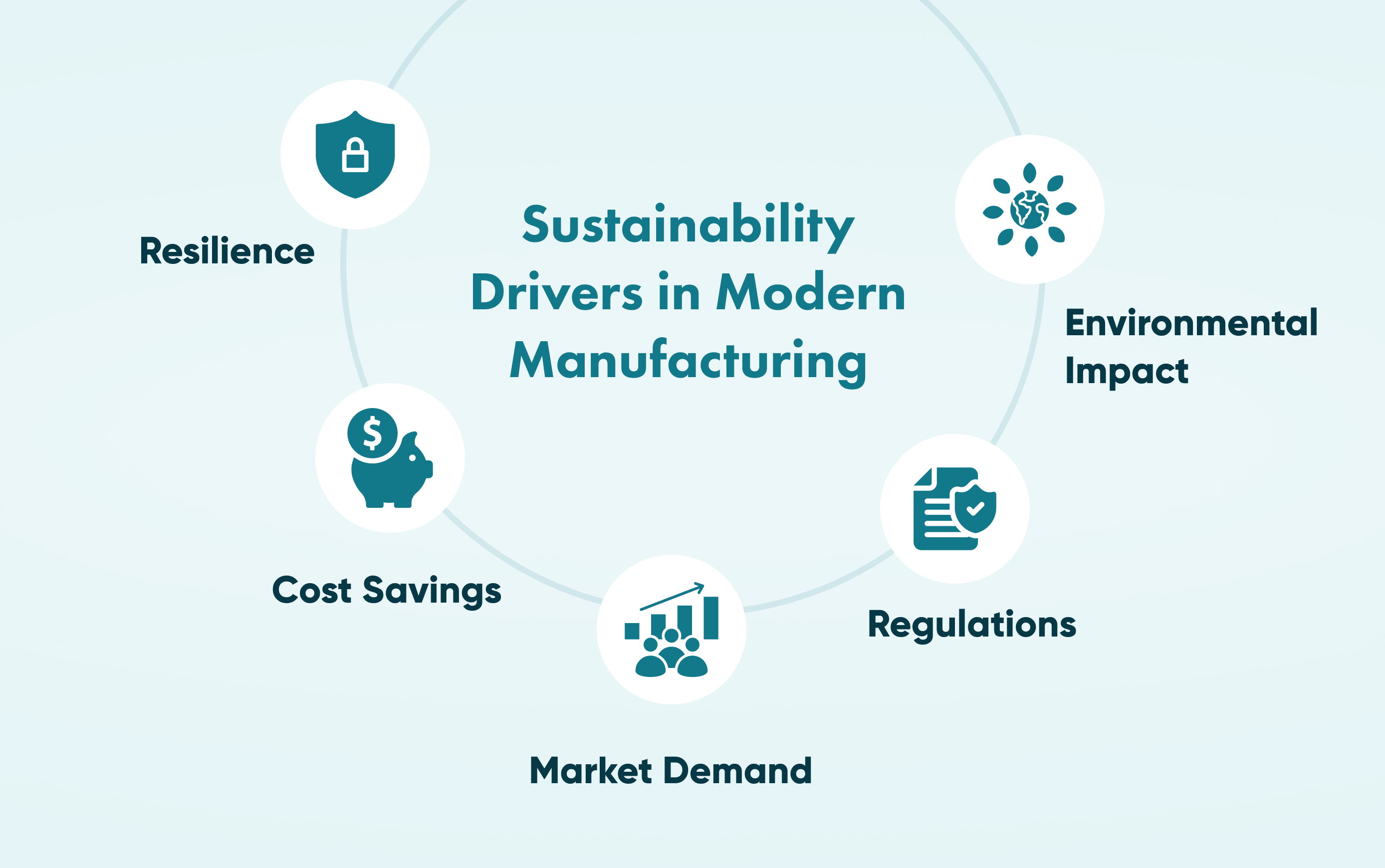
Key Benefits and Drivers for Change and Accelerating Innovation:
- Environmental impact: the use of cleaner energy and the reduction of waste result in less pollution, help in meeting climate targets, and support the preservation of natural resources.
- Regulations: the EU Green Deal and CSRD, for instance, impose requirements such as carbon reporting, emissions reduction, and giving freedom to stakeholders to control the activities through transparency.
- Market pressure: about 72% of consumers are more willing to buy products from environmentally friendly companies; thus, green companies enjoy brand trust and easy access to investors.
- Cost savings: production equipment that consumes energy efficiently, recycling units, and lean, economically viable processes improve the company's cost-effectiveness and, at the same time, contribute to better profit margins by lessening the company's long-term operational expenses.
- Resilience: the use of circular supply chains, as well as sustainable design, can lead to the arrival of new ideas and the securing of future operations.
How AI Enables Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
AI and machine learning are two of the most important technologies that can be used to make data-driven decisions in environmentally friendly manufacturing. These technologies gather real-time data from sensors and machines and then use the data to optimise processes, enhance efficiency, and even allow for proactive resource management. Along with data automation, AI and machine learning can efficiently use energy and reduce waste to produce more circular and resource-saving production processes.
How Does AI Optimise Energy Consumption?
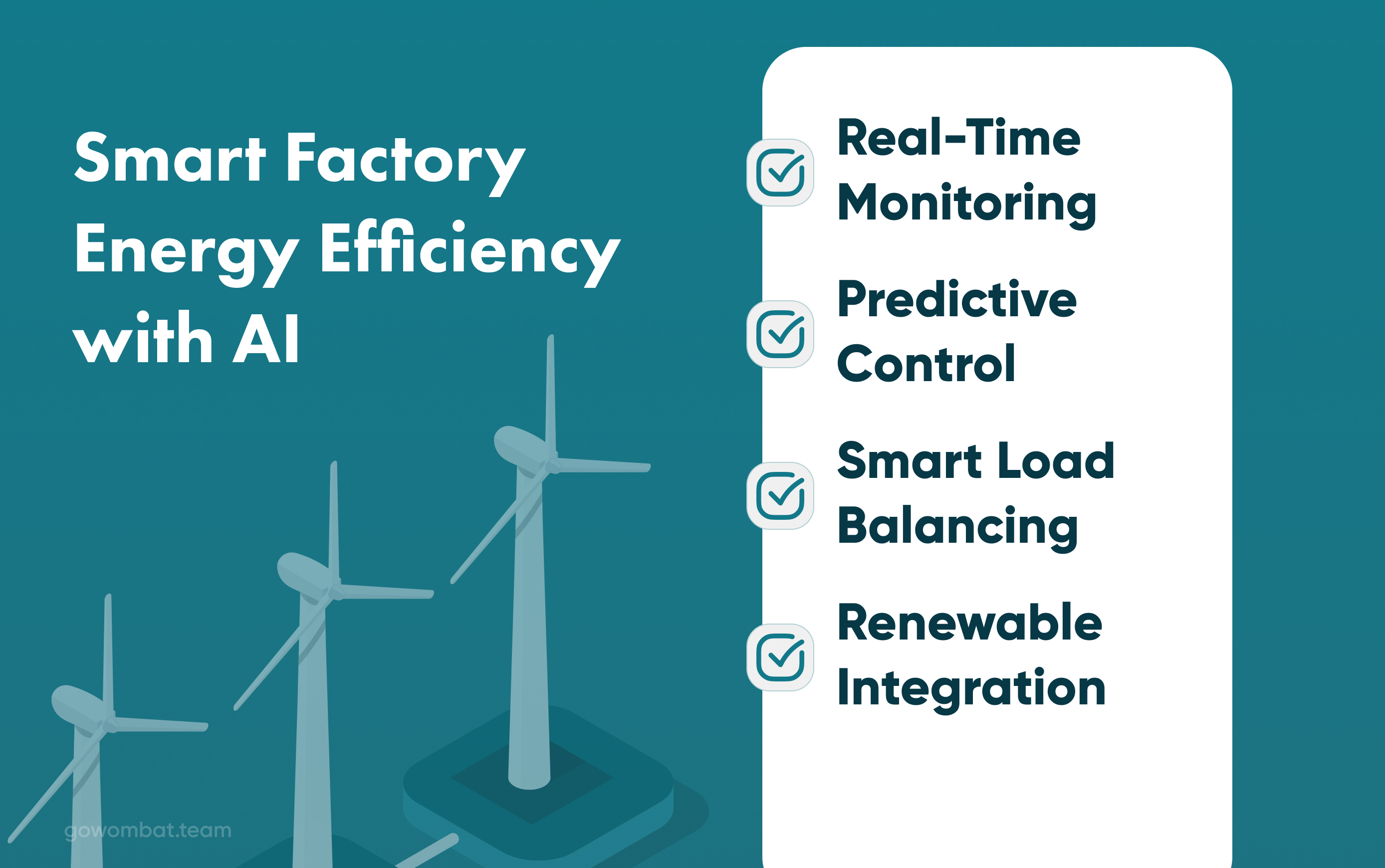
AI energy management systems provide manufacturers with the same cut power usage capabilities through real-time analysis and control. Intelligent platforms dynamically change lighting, heating, and machines - thus, energy is only consumed when it is necessary. Besides, AI also optimises energy systems and handles the total capacity of manufacturing facilities, leading to better efficiency. The largest energy consumers, data centres, are becoming the focus of green AI solutions as they converge on a sustainable future and minimise negative environmental impact.
- Interaction with the environment on a minute-to-minute basis
Non-critical work is scheduled by AI for a time when electricity demand is low.
- Predictive control
AI anticipates changes in demand and prepares systems for it. Digital twins are used to try out energy management solutions in a virtual environment.
- Renewables integration
Green AI is a lever to the development of clean energy systems by matching the production of solar/wind power so that clean energy can be fully utilised.
How Does AI Reduce Waste in Production?
Artificial intelligence improves the quality of products and the efficiency of processes, thus reducing the waste of materials and scrap. AI-driven production lines are one of the most extreme cases of AI usage in quality improvements. The McKinsey quality report states that they cause '99% defect reduction' and up to 70% less waste.
One of AI's main contributions to quality improvement is that it detects defects at an early stage and accurately forecasts failures through the complete automation of data collection and processing. It enables sufficient cost-cutting and efficiency-improving activities. With the assistance of AI-driven solutions, there is less human intervention in these workflows. Thereby, human error in repetitive tasks is reduced, and the quality and reliability of the processes are enhanced. Processes are also optimised in that equipment is made more efficient by identifying and eliminating the most costly defects, speeding up and optimising processes, and reducing waste and energy costs. That is bringing operational costs down to a minimum by reallocating resources to better positions of the business.
- Computer vision inspection
It uses image recognition at extreme speed to locate defects on the spot.
- Predictive maintenance
Interprets sensor data to avoid failure and the use of products that are not up to standard; thus, human intervention is less needed, and the risk of human error is lowered.
- Process optimization
By studying previous operations, it finds the ways through which it can reduce the production of the off-spec materials by looking through the historical data.
- Inventory and supply forecasting
Not only does it stop overproduction from happening, but it can also perfectly plan the material orders.
How Does AI Support Circular Manufacturing?
By using AI in circular manufacturing, the system enhance the design, reuse and reverse logistics of manufactured products so that they can stay in the loop for longer, cut costs, and the consumption of resources can be minimised:
- Design optimisation: generative AI invents the component using minimal material, making it more recyclable.
- Lifecycle tracking: AI estimates product end-of-life and facilitates recycling local logistics.
- Reverse logistics: optimises the collection and remanufacturing of returns.
- Repair forecasting: identifies the repair or replacement of machines or parts that are close to failure.
How Does Data Automation Improve Resource Efficiency?
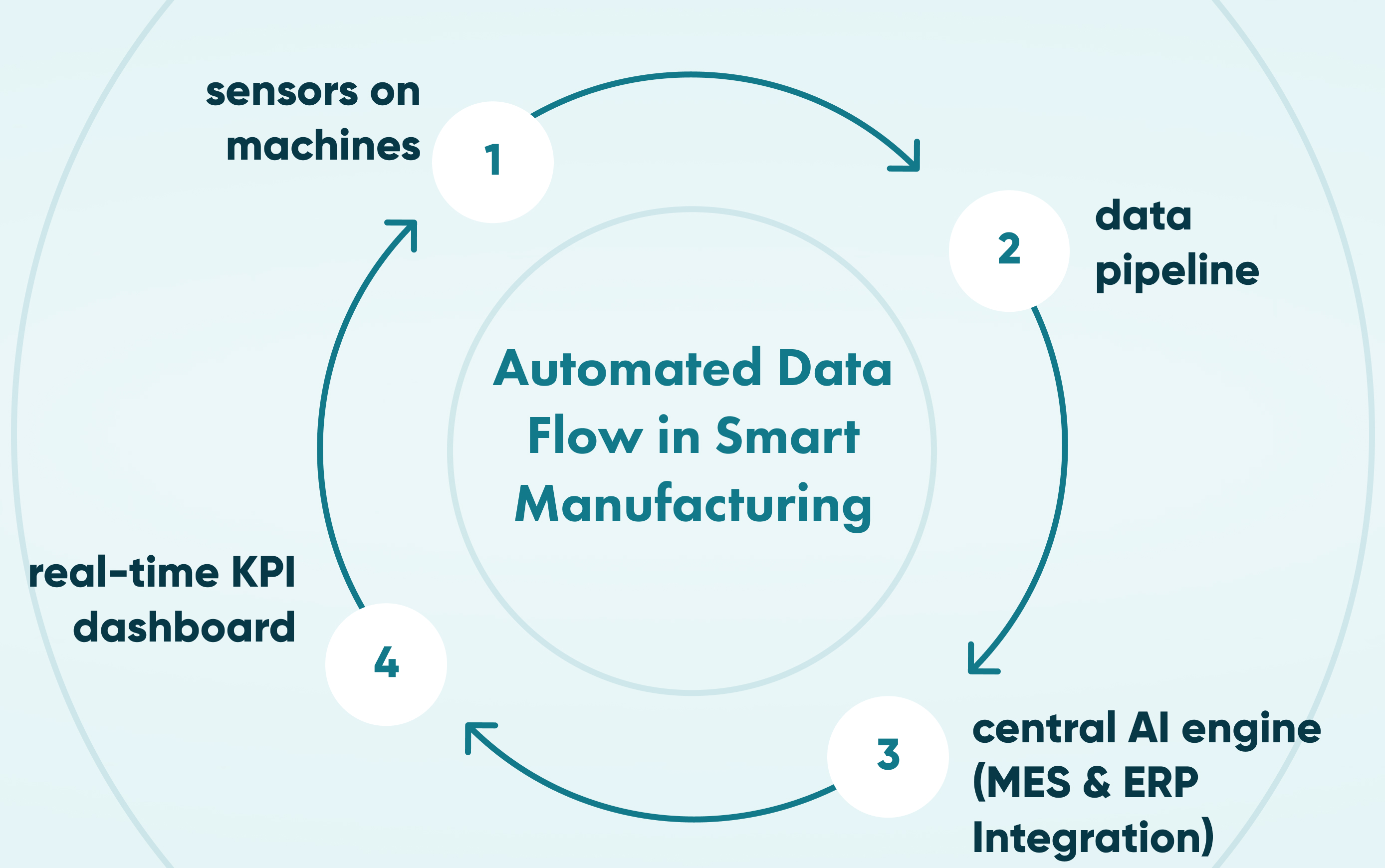
Data automation tools have the ability to collect and integrate massive amounts of data from a wide range of sources, such as production, factory floor, sales and other business operations, thereby giving a complete picture of manufacturing performance. Data extracted from these sources is deposited in a data warehouse for simplified analysis and reporting. In this way, companies become capable of handling huge volumes of data from various sources in an efficient manner. In turn, this leads to them being able to make their decisions faster, analyse with more accuracy, and optimise with AI:
- Real-time insights: dashboards help managers to recognise waste, inefficiencies, or abnormal usage.
- Scalable consistency: the use of automation technology gets rid of manual mistakes, especially in repetitive tasks, and can grow with output increase.
- AI integration: uninterrupted data streams allow AI algorithms to change production on the fly (e.g., by energy pricing or weather).
Comparative Impact of AI-Driven Sustainable Manufacturing
Let’s compare two manufacturers. Company A actively uses AI across its operations, while Company B relies on traditional, non-AI-driven processes.
Energy costs • Company A: reduce energy costs by 20–30% through real-time optimisation and intelligent energy management. • Company B: energy costs increase due to inefficient scheduling and a lack of real-time control.
Downtime and repairs • Company A: reduce downtime by around 25% through predictive maintenance and early fault detection. • Company B: experiences higher downtime caused by unexpected breakdowns and reactive maintenance.
Material waste • Company A: reduce material waste by up to 70% using AI-driven defect detection and quality control. • Company B: generate more waste due to overproduction, late defect detection, and poor quality control.
Decision-making speed • Company A: improve decision-making speed by 30–50% through automated analytics and real-time insights. • Company B: slower decision-making caused by manual data handling and fragmented information.
Compliance reporting • Company A: streamline compliance through automated reporting, dashboards, and real-time data collection. • Company B: compliance reporting is time-consuming, manual, and prone to errors.
Operational scalability • Company A: scale operations more easily using data pipelines, automation, and AI models. • Company B: scalability is limited and heavily dependent on manual effort.
Supply chain resilience • Company A: strengthen supply chains with AI-driven demand forecasting and predictive planning. • Company B: supply chains remain vulnerable due to reactive planning and limited visibility.
Brand and investor appeal • Company A: achieve higher brand trust and investor interest through ESG alignment and transparency. • Company B: lower credibility and reduced access to sustainability-focused investors.
Profit margins • Company A: improve profit margins by optimising efficiency, reducing waste, and lowering operational costs. • Company B: profit margins remain under pressure due to inefficiencies and higher operating expenses.
AI-powered factories are delivering better results in terms of costs, compliance, profits, and climate goals than their traditional counterparts, thus leading to energy savings and waste reduction, among other things, along with resilience, innovation, and often customer experience. The return on investment is quite evident as well.
Benefits and Limitations of AI-Driven Sustainability
AI-driven sustainability in manufacturing brings a lot of good things along but also some drawbacks.
Pros:
- Energy costs can be lowered substantially by optimised consumption
- The waste generation and emissions that contribute to global warming are reduced
- The safety in the work environment is improved by the removal of the hazardous or monotonous tasks through automation
- The accurate forecasting tools that are used provide valuable insights and can help maintenance and management become more proactive
Cons / Barriers:
- Problems with data quality and the existence of data silos can be factors that slow down AI implementation
- The high costs for the first integration and the complexity with old systems may cause problems
- There is a gap in skills, as most manufacturers do not have expertise in AI and data analytics
- The need for governance and transparency to secure the responsible use of AI and customer rights
Practical Steps to Implement AI for Sustainable Manufacturing
Manufacturing enterprises aiming at adopting AI for sustainability could implement these steps one by one:
- Evaluate energy and waste hotspots in manufacturing processes to discover potential areas of improvement
- Construct a strong IoT data layer to allow extensive data gathering and monitoring
- Combine databases by integrating ERP, MES, and IoT systems to eliminate data silos
- Locate extremely impactful predictive uses, such as maintenance or quality control
- Use pilot projects initially to confirm AI-powered solutions and then consider scaling
- Create sustainability KPI tracking systems with the help of dashboards in real time
- Enable data literacy through training business users and operators
- Put in place AI governance structures to maintain the deployment of AI ethically, transparently, and responsibly AI
Conclusion / Key Takeaways
AI is an essential tool of economically sound processes of sustainability, nowadays used by industry and business leaders.
- Sustainable manufacturing utilizes AI and data automation to achieve energy efficiency, decrease waste, and lower the carbon footprint of the process.
- AI allows for on-demand monitoring, forecasting, and closed-loop manufacturing data that enable sustainability initiatives to be sustained and expanded.
- Data automation is key to resource saving as it makes the collection, processing, and reporting of data across different production operations quick and easy.
- Discover how AI-powered solutions can be a lever for your sustainable production through our manufacturing development services page and make your next move towards a green future.
The team at Go Wombat is deeply knowledgeable in AI development for manufacturing and industrial sectors. We work with you to create tailored AI solutions and data-automation platforms that lead to exactly these types of sustainability and environmental benefits - lowering energy consumption, waste minimisation, and resource optimisation. Get in touch with us if you want to know how our AI proficiency can help your factory become more intelligent, environmentally-friendly, and cost-effective.
Unlock Success with Premium Software Development
Contact us


FAQs
How does AI contribute to environmentally friendly manufacturing?
AI is a major factor in promoting environmentally friendly manufacturing by managing and optimising the use of energy, thus decreasing waste, conserving energy, enabling the practice of predictive maintenance, reducing costs, and even supporting circular production models. It does so by using data collected and analytics from production lines to make the most informed and efficient choices that help protect the environment.
What kinds of data do manufacturers need to automate sustainability?
Manufacturers need various types of data, such as energy consumption data, production metrics, information about the supply chain, and parts of the data that are unstructured and come from the sensors. The combination of past data with the live data collected from IoT devices provides the foundation for AI-driven initiatives of sustainability that are effective.
Why is the use of predictive maintenance so vital to sustainability?
Predictive maintenance allows the reduction of machine downtime and the prevention of sudden failures, which leads to energy and raw material savings. By predicting equipment problems, many manufacturers are able to schedule repairs in a more efficient way, thus prolonging the lifespan of assets and reducing waste.
What are the obstacles to using AI for achieving sustainability?
The obstacles to utilising AI for achieving sustainability may be problems surrounding unstructured data, its quality and integration, the situation where costs are high at the start, issues regarding old system complexities, a shortage of skilled personnel, and the requirement for clear governance to ensure ethical use of AI.
In what ways could a small or mid-sized manufacturer initiate AI sustainability projects?
A few practical first steps would be starting with pilot projects that focus on a specific use, such as energy monitoring or quality control; thus, building the IoT data foundation by training teams on data literacy. By using cloud-based AI solutions, many businesses can also lower the upfront investment and the complexity of the project.
How can we help you ?




